Rolling Bearings - Key Solutions for Industry and Machinery
At Simmering.pl, we offer a comprehensive selection of rolling bearings essential for a wide variety of industrial applications. Rolling bearings play a crucial role in ensuring smooth movement, reducing friction, and extending the lifespan of machinery components. Whether you are dealing with high-speed rotations, heavy loads, or precise alignment, our range of bearings is designed to meet your needs with reliability and efficiency.
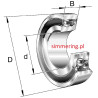
Construction of Rolling Bearings
Rolling bearings consist of three main components:
- Inner ring: Mounted on the shaft.
- Outer ring: Installed in the housing or frame.
- Rolling elements: Balls, rollers, or needles that reduce friction between the rings.
Additionally, many bearings come equipped with cages that keep the rolling elements evenly spaced and seals that protect against contaminants and lubricant loss.
Applications of Rolling Bearings
Rolling bearings are versatile and suitable for various applications across multiple industries:
- Ball bearings: Universal bearings ideal for a wide range of industrial uses.
- Tapered roller bearings: Designed to handle significant radial and axial loads, perfect for precision applications.
- Cylindrical roller bearings: Best suited for high-speed rotations and axial loads.
- Spherical roller bearings: Excellent for large shafts and high-load applications.
- Needle roller bearings: Perfect for high-speed, radial-load applications in compact spaces.
Classification of Rolling Bearings
Rolling bearings can be classified based on:
- Type of rolling elements: Balls, rollers, spherical rollers, or needles.
- Load direction: Radial, axial, or combined loads.
- Arrangement: Standard, self-aligning, or adjustable.
Common Issues and Diagnostics of Rolling Bearings
Causes of bearing failure include:
- Improper installation: Can lead to scratches or dents.
- Excessive load: May cause damage to the raceways.
- Contamination: Can result in corrosion or operational issues.
Diagnostic methods:
- Vibration analysis: Measures RMS and FFT vibration spectra.
- Temperature measurement: Helps detect excessive heat levels.
- SPM HD method: Provides precise diagnostics of bearing condition and lubrication quality.
FAQ:
-
What are the main types of rolling bearings?
The main types include ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, and needle roller bearings, each suited to specific load types and applications. -
What are the most common causes of rolling bearing failures?
Common causes include improper installation, excessive loads, contamination, and inadequate lubrication. -
What are the best methods for diagnosing bearing issues?
Effective diagnostic methods include vibration analysis, temperature measurement, and the advanced SPM HD method for assessing bearing condition and lubrication. -
How can I maintain rolling bearings to prevent failure?
Regular lubrication, keeping bearings clean, and ensuring proper installation are essential for prolonging the life of rolling bearings and maintaining optimal performance.
Keywords:
rolling bearings, ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, cylindrical bearings, spherical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, bearing construction, bearing applications, bearing diagnostics, bearing maintenance, bearing seals, bearing cages, rolling bearing failures