Materials Used in O-Rings – A Comprehensive Guide for Customers
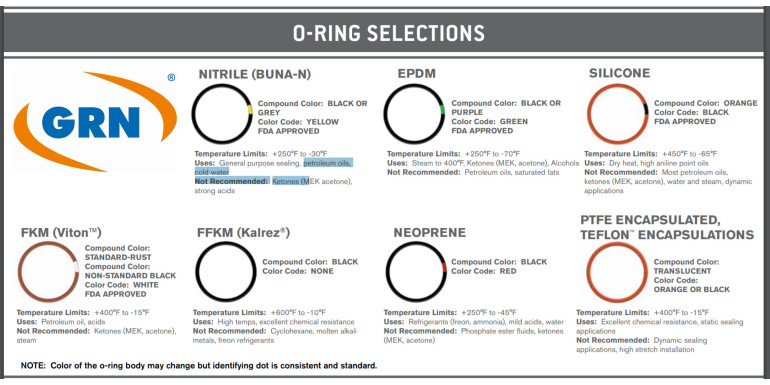
O-rings are crucial sealing components used across industries, including automotive, industrial, and household appliances. Choosing the right material is essential for the efficiency and longevity of an O-ring. Below is a detailed overview of the most popular elastomer materials used in O-ring manufacturing, along with their properties and applications.
| Material | Temperature Range | Characteristics | Applications | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NBR (Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) | -40°C to +100°C (short-term up to +120°C) | - Flexible - Resistant to oils, fuels, lubricants - Low deformation |
Automotive industry, oil and hydraulic systems. Not resistant to glycol-based brake fluids. | Black |
| VMQ (Silicone Rubber) | -60°C to +210°C (short-term up to +250°C) | - Excellent resistance to air, oxygen, ozone, water - Great electrical insulation - Fire-resistant |
Food, pharmaceutical, home appliances, static seals. | Red, white, transparent |
| EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Rubber) | -50°C to +150°C | - Excellent resistance to brake fluids, steam, detergents, acids, bases - Not resistant to mineral oils |
Brake systems, home appliances, sanitary equipment. | Black |
| FPM/Viton (Fluoroelastomer) | -20°C to +205°C (short-term up to +230°C) | - High chemical and heat resistance - Resistant to oils, fuels, UV radiation, ozone |
Aerospace, chemical industry, high-temperature seals. | Black, green, brown |
| HNBR (Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber) | -30°C to +150°C | - High abrasion resistance - Strong tensile strength - Resistant to oils and fuels |
HVAC systems, home appliances, automotive industry. | Black, green, violet |
| PTFE (Teflon) | -200°C to +200°C (short-term up to +260°C) | - Very low plasticity - High chemical resistance - Low friction |
Chemical, pharmaceutical, petrochemical industries. | White |
| FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) | -20°C to +300°C (short-term up to +325°C) | - Exceptional chemical resistance - High-temperature resistance |
Aerospace, oil extraction, analytical instruments. | Green, black |
Choosing the Right O-Ring Material O-rings, also known as sealing rings, are made from various elastomer materials that influence their durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals and temperatures. Popular materials like NBR, FPM, EPDM, HNBR, and PTFE play a vital role in O-ring performance across different applications. When selecting an O-ring, it’s essential to consider temperature range and the medium it will seal. The right material ensures long-lasting performance and minimizes the risk of failure.
At Simmering.pl, we offer a wide range of O-rings made from elastomers like NBR (ideal for oils and lubricants), FPM (for high temperatures and chemicals), HNBR (abrasion resistance), and PTFE (excellent chemical resistance). Explore our catalog to find the perfect product for your application.
FAQ:
1. Which O-ring material is best for high temperatures?
- FPM (Viton) O-rings are suitable for high temperatures up to +205°C, with short-term resistance up to +230°C. FFKM O-rings can withstand up to +300°C.
2. Are NBR O-rings resistant to oils?
- Yes, NBR O-rings are highly resistant to oils, fuels, and lubricants, making them a popular choice for automotive and hydraulic applications.
3. What colors do silicone O-rings come in?
- Silicone (VMQ) O-rings are available in red, white, and transparent. They are commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
4. Can PTFE O-rings be used in chemical applications?
- Yes, PTFE O-rings offer excellent resistance to most chemicals, but they should be avoided in environments with fluorine gas or molten alkali metals.
5. What are HNBR O-rings used for?
- HNBR O-rings are commonly used in HVAC systems and home appliances due to their abrasion resistance and compatibility with mineral oils.




Leave a Reply Cancel Reply